Basic Earnings Per Share EPS: Definition, Formula, Example
Stock buybacks and new stock issuance are two methods for publicly-traded companies (post-IPO) to directly impact their number of outstanding shares. Suppose we’re tasked with calculating the earnings per share (EPS) of a company that reported $250 million in net income for fiscal year 2021. The section will contain the EPS figures on a basic and diluted basis, as well as the share counts used to compute the EPS. It’s a straightforward way to assess profitability, as it takes the complexities of the income statement and distills it into one simple number.
Basic Earnings Per Share (EPS): Definition, Formula, Example
Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others. Investors know that without risks, there would be no rewards, but brilliant investors do not take any chance by investing in a company they are unsure about.
) Retained Earnings Per Share
Preferred shares, on the other hand, provide preferred shareholders with no voting rights. If a company ever has to liquidate, common shareholders are the last group of people who can make claims. If a firm goes bankrupt due to bankruptcy, common stockholders receive nothing. From an investment standpoint, common stockholders usually profit more handsomely in the long run. Some shares may be acquired by public members, whereas others are only available to certain people in the company.
- One of the first performance measures to check when analyzing a company’s financial health is its ability to turn a profit.
- The earnings per share (EPS) is the portion of a company’s total profit allocated to each of the shares held by the company’s shareholders.
- If a firm is liquidated, the book value earnings per share are enough to calculate the worth of each share.
- Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching.
Current EPS
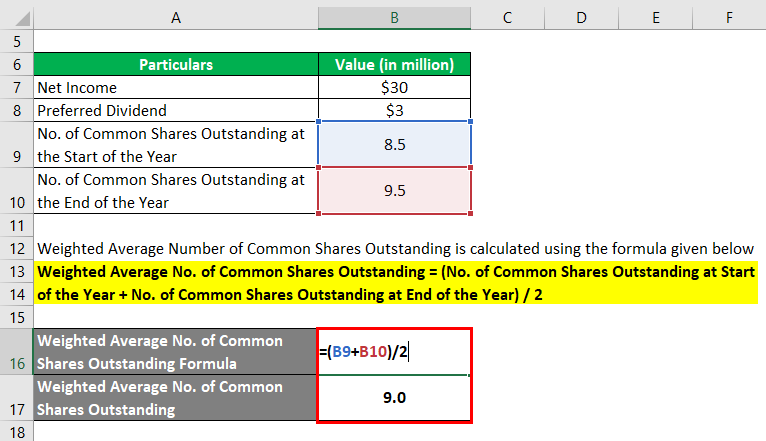
ABC also has 1 million stock options outstanding with an exercise price of $10, while its stock trades at $20. For both basic EPS and diluted EPS, the earnings figure should be the same. A basic share count equals the average count of only the shares that are issued and outstanding during the period. Thus, we use the weighted average common shares to account for this time difference.
Basic Earnings Per Share Calculation Example (EPS)
In case of loss, the preferred dividend is added to increase the amount of net loss. Indeed, investors and analysts largely rely on the Basic EPS to assess the performance of the company over time. This measure is reported in the company’s Income Statement, usually along with the Diluted EPS which is a calculation of the Earnings per Share that considers the effect of stock options and warrants. Earning per share (EPS), also called net income per share, is a market prospect ratio that measures the amount of net income earned per share of stock outstanding. In other words, this is the amount of money each share of stock would receive if all of the profits were distributed to the outstanding shares at the end of the year.

Part 2: Your Current Nest Egg
The method to calculate Basic EPS is very simple if the analyst knows the net income or net earnings of the period and the number of outstanding shares at the end of such period. EPS stands for earnings per share, which is the amount of a company’s net earnings per share of outstanding stock. That is why you should look at the P/E ratio (Price/Earnings ratio) and basic EPS.
Since we now have the beginning and ending number of common shares outstanding, the next step is to calculate the weighted average shares outstanding. Throughout fiscal year 2021, the company issued no new shares and repurchased 20 million shares, resulting in 140 million common shares outstanding at the end of the period. From that starting what is taxable and nontaxable income point, the diluted shares are determined by compiling a company’s potentially dilutive securities such as options, warrants, restricted stock units (RSUs), and convertible debt instruments. The Earnings Per Share (EPS) is the ratio between the net profit generated by a company and the total number of common shares outstanding.
It includes not only those shares already issued, but those that likely will be in the future. It adds shares to the count usually based on the treasury stock method, which accounts for the cash that would be generated by the company through option and/or warrant exercise. Earnings per share is an important metric used by investors and analysts to evaluate a company’s financial performance.

